OpenAI has launched a web crawler to ‘potentially’ improve the future models, the company announced in a blog post. The reference to future models here doesn’t necessarily means GPT-5. The company may use it to make improvements in GPT-4 as well.
After facing criticism for scraping paywalled content from various prominent publications—some of which are actively seeking ways to challenge the company—OpenAI has announced that their newly launched web crawler will be configured to filter out sources that demand paywall access. It will also eliminate sources that are recognized for collecting personally identifiable information (PII) or containing text that violates OpenAI’s policies.
“Allowing GPTBot to access your site can help AI models become more accurate and improve their general capabilities and safety,” stated the company in its announcement.
OpenAI has also provided instructions for website owners who wish to entirely prevent the GPTbot from crawling their websites. They also have the option to restrict access to specific areas of their websites while still permitting the crawler to scan the remaining content.
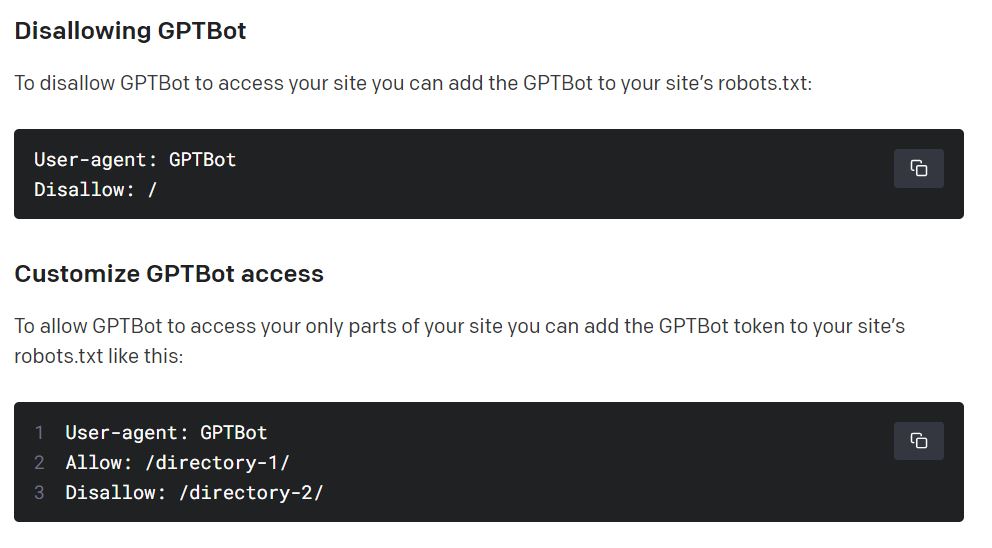
What is interesting here is that OpenAI has been scraping the internet for years, reportedly using Common Crawl, to train its large language models, without obtaining consent from the publishers or website owners. While technically publishers could have prevented this by making minor adjustments to their robots.txt files, few were aware that their data was being harvested for the purpose of training these large language models.
It remains to be seen whether the motivation for OpenAI to launch this crawler with controls for site owners stems from a desire to do good, pressure from various stakeholders, or something completely different.






